“Does creatine expire?” is a question that resonates deeply among fitness enthusiasts and athletes who rely on this potent supplement to enhance their performance. As the fitness industry continually evolves, so does our understanding of the products we ingest. Creatine, recognized for its myriad benefits in muscle growth and energy output, is no exception. However, like all nutritional supplements, its effectiveness and safety over time come under scrutiny.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of creatine—from its origins to its shelf life, highlighting its storage, signs of degradation, and expert opinions on its expiration. Join us as we navigate the facts behind creatine’s longevity and its implications for your fitness journey.
Table of Contents
What is Creatine?
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found in small amounts within our bodies, mainly in the muscles. It’s composed of three amino acids: arginine, glycine, and methionine. Its primary function? To help produce energy quickly during high-intensity, short-duration activities, like lifting weights or sprinting.
Here’s a simple breakdown of how creatine works:
- Our muscles use a molecule called ATP (adenosine triphosphate) for energy.
- Once ATP releases its energy, it turns into ADP (adenosine diphosphate).
- Creatine, stored in the muscles as creatine phosphate, donates its phosphate group to ADP, turning it back into ATP.
In other words, creatine acts as a reserve for phosphate groups, ensuring that ATP production is efficient, especially during brief, intense activities.
Due to its energy-boosting properties, creatine has become a staple supplement for athletes, bodybuilders, and fitness enthusiasts. It’s available in several forms, with creatine monohydrate being the most researched and commonly consumed.
Benefits of Creatine Include:
- Improved exercise performance.
- Increased muscle mass.
- Enhanced brain health.
Given its significant benefits and the extensive research supporting its safety and efficacy, creatine has earned its spot as one of the most popular and trusted dietary supplements worldwide.
The Popularity of Creatine in Fitness
Creatine’s rise to fame in the fitness world is nothing short of remarkable. With its scientifically-backed benefits and practical applications, it has established itself as a must-have for those looking to optimize their performance and results. But what’s behind the immense popularity of creatine in fitness circles?

- Performance Enhancement: Creatine has been consistently shown to boost performance in high-intensity, short-duration activities. This means athletes, from sprinters to weightlifters, can see measurable improvements in their training sessions. It enables them to push harder, lift heavier, and sprint faster.
- Muscle Growth: Alongside its performance-enhancing properties, creatine plays a significant role in muscle hypertrophy. It increases the water content within muscle cells, creating a more anabolic environment. Moreover, creatine can elevate certain hormones that promote muscle growth, such as IGF-1.
- Quick Results: Many individuals report seeing and feeling the benefits of creatine supplementation in as little as a week. This quick turnaround is particularly motivating for those who are keen on seeing rapid progress.
- Extensive Research: The sheer volume of studies on creatine stands testament to its efficacy and safety. The fitness community appreciates supplements that are backed by hard science, and creatine certainly fits the bill.
- Cost-Effective: Unlike many supplements with hefty price tags, creatine is relatively affordable. This cost-effectiveness, combined with its proven benefits, makes it an attractive choice for many.
- Versatility: Creatine isn’t just for bodybuilders or elite athletes. Its benefits extend to a variety of sports and activities, from football to martial arts and even endurance sports, albeit to a lesser extent.
Given these compelling reasons, it’s no wonder that creatine has cemented its place in the fitness industry. Walk into any gym, and it’s likely that a good portion of the members have, at some point, incorporated creatine into their supplement regimen.
It’s crucial to remember that regular creatine use necessitates increased water consumption to maintain adequate hydration levels, ensuring the supplement’s effectiveness and your overall health.
Understanding Expiry Dates
Before diving into the specific details regarding whether creatine expires, it’s crucial to grasp the general concept of expiry dates. The expiry date, sometimes labeled as the “best before” or “use by” date, offers a guideline about the time until which the product maintains its intended quality and potential health benefits.

- Meaning of Expiry Date: Contrary to popular belief, the expiry date isn’t necessarily a point at which the product becomes harmful or dangerous to consume. Instead, it indicates that the product may begin to lose its potency or effectiveness after this date. For many products, including supplements, the active ingredients might degrade over time.
- Safety vs. Potency: Post the expiry date, the primary concern with many products isn’t safety but rather efficacy. The product may still be safe to consume, but it might not offer the same benefits as it would have if consumed before the date.
- Factors Influencing Expiry: Several factors can determine a product’s expiry date. These include the nature of the active ingredient, the product’s formulation, the storage conditions, and the packaging type. For instance, products kept in cool, dry places tend to have longer shelf lives than those exposed to moisture and heat.
- Regulatory Standards: Expiry dates are also influenced by regulatory standards and guidelines. Manufacturers must perform stability tests to determine how long their product maintains its quality. This ensures that consumers get a product that meets certain standards up to the indicated expiry date.
- Recommendation: While some products may still be effective post their expiry dates, it’s always recommended to consume products, especially health supplements, within the specified timeframe. This guarantees that you’re obtaining the maximum benefits and aren’t consuming anything that might have degraded.
Practical Implications for Creatine: Since creatine is a popular supplement, understanding expiry dates becomes even more critical. While creatine’s chemical structure is stable, external factors, storage conditions, and its formulation can influence how long it remains effective.
Does Creatine Expire?
The burning question on many fitness enthusiasts’ minds: does creatine expire? The straightforward answer is yes, like all dietary supplements, creatine does have an expiry date. But understanding what this means in practical terms is essential for those looking to maximize their workouts and maintain safety.

- Creatine Stability: Creatine, in its pure form, is a relatively stable compound. When stored correctly, it doesn’t degrade quickly. However, the efficiency and potential benefits of creatine can diminish over prolonged periods, especially if exposed to unfavorable conditions.
- Decoding the Expiry Date: An expiry date on a creatine supplement is the manufacturer’s guarantee that the product will retain its labeled potency and purity up to that date. Beyond this date, the creatine may still be safe to consume, but its efficacy could be reduced.
- Factors Affecting Expiry: The longevity of creatine is influenced by factors like moisture, heat, and exposure to air. For instance, if creatine is stored in a damp environment, it can convert to creatinine, a less effective by-product. This transformation isn’t harmful but can diminish the supplement’s benefits.
- Physical Changes: One indication that creatine may be past its best is if there are noticeable changes in its appearance or texture. For example, if your creatine powder has clumped together, it may have been exposed to moisture.
- Usage Beyond Expiry: While it’s recommended to consume creatine before its expiry date for maximum effectiveness, using it slightly beyond this date might not be harmful. However, always ensure there are no signs of spoilage or unusual odors, and when in doubt, it’s safer to discard the product.
- Best Practices: To ensure your creatine remains potent for as long as possible:
- Store it in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight.
- Ensure the lid or seal is closed tightly after each use.
- Avoid using wet utensils to scoop out the powder.
In summary, while creatine does have an expiry date, it often pertains more to the product’s effectiveness rather than safety. However, always prioritize your health by adhering to recommended usage guidelines and storage practices.
How to Store Creatine Properly
Ensuring the longevity and potency of your creatine supplement begins with understanding how to store it correctly. Proper storage not only extends the shelf life of creatine but also ensures that you get the most out of every scoop. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to store creatine properly:

- Cool and Dry: One of the primary enemies of creatine’s stability is moisture. Always store your creatine in a cool, dry place, away from areas with high humidity like bathrooms or kitchens.
- Away from Direct Sunlight: Prolonged exposure to sunlight can degrade the quality of creatine. Keep the container in a cupboard, drawer, or any location that doesn’t get direct sunlight.
- Tightly Sealed: Every time you use your creatine, make sure to close the lid or seal the bag tightly. This action prevents air and moisture from entering and degrading the product.
- Original Packaging: It’s advisable to keep creatine in its original packaging. Manufacturers design these containers to protect the contents from external factors. If you must transfer it, use an airtight, opaque container.
- Avoid Contamination: Always use clean, dry utensils to scoop out your creatine. Introducing wet spoons or scoopers can accelerate the degradation process.
- Temperature Consistency: While storing creatine in a cool place is ideal, it’s essential to avoid places with fluctuating temperatures, like garages. Consistent temperatures help maintain the product’s stability.
- Keep Away from Strong Odors: Creatine is best stored away from areas where it could absorb strong odors, such as near spices or aromatic foods.
- Bulk Storage: If you buy creatine in bulk, consider dividing it into smaller portions. Store the main quantity in a cool, dry place and keep a smaller amount for daily use. This practice minimizes the exposure of the entire product to external elements.
- Check Regularly: Every so often, check the creatine’s texture and smell. If it starts to clump, appears discolored, or emits an unusual odor, it might be time to replace it.
In essence, storing creatine properly ensures you’re always consuming a potent and safe product. Given its importance in many fitness regimes, it’s worth the few extra moments to ensure it’s stored in the best possible conditions.
Signs That Creatine Has Degraded
Creatine, like any other dietary supplement, has a shelf life, and it’s essential to know when it may have degraded to avoid consuming an ineffective or, in rare cases, harmful product. Here are some clear indicators that your creatine may have degraded or is past its prime:

- Clumping: One of the most evident signs is when your creatine starts to form hard clumps. Creatine is usually a fine powder, and clumping can indicate that moisture has found its way into the container, which can lead to degradation.
- Discoloration: Fresh creatine is typically a white or off-white color. If you notice any yellowing or other discolorations, it could be a sign that the product has been compromised.
- Unusual Odor: Creatine has a very mild odor, if any at all. If your supplement starts to emit a strong or off-putting smell, it might be time to discard it.
- Change in Taste: While creatine is usually tasteless or has a slightly bitter taste, a pronounced sour or off taste can indicate degradation.
- Ineffectiveness: If you’ve been using creatine for a while, you might be familiar with its effects on your workouts. A noticeable decrease in its effectiveness might be a sign of the product’s decreased potency.
- Settling or Separation: If you notice that your creatine doesn’t mix as well as it used to in water or other liquids, or if there’s a significant amount of sediment at the bottom, this could be a sign of degradation.
It’s essential to always prioritize safety and efficacy when consuming any supplement. If you suspect that your creatine has degraded, it’s better to err on the side of caution and replace it. Remember, consuming degraded creatine might not only be ineffective but could also lead to potential digestive discomfort.
Impact of Consuming Expired Creatine
Creatine is a popular supplement among fitness enthusiasts and athletes for its ability to enhance performance and support muscle growth. But like all supplements, it has a shelf life. If you’ve found an old tub of creatine in your pantry and are wondering about the implications of consuming it, here’s what you need to know:

- Reduced Efficacy: One of the primary concerns with expired creatine is that it may lose its potency over time. This means that you might not experience the same energy boost, improved workout performance, or other benefits that fresh creatine typically offers.
- Digestive Discomfort: Consuming degraded creatine can lead to digestive issues such as stomach cramps, bloating, and diarrhea. This can be due to the breakdown products formed when creatine degrades or because of contaminants introduced due to improper storage.
- Potential Harmful Compounds: Over time, and especially in the presence of moisture, creatine can break down into a substance called creatinine. While creatinine is naturally found in the body and is typically harmless, in larger amounts, it can put strain on the kidneys as they work to filter it out.
- Loss of Money: While not a health impact, using an ineffective product means you’re not getting the bang for your buck. It might make more financial sense to invest in a fresh batch rather than using an old one with reduced or no benefits.
- Allergies or Sensitivities: Any product, including creatine, that has been stored improperly or for an extended period, can become contaminated. Consuming such products can lead to allergic reactions or sensitivities in some individuals.
To ensure safety and effectiveness, always check the expiration date of your creatine and store it as per the manufacturer’s guidelines. If in doubt, it’s always best to err on the side of caution and avoid consuming expired supplements.
Difference Between Creatine Degradation and Contamination
Understanding the difference between creatine degradation and contamination is essential for anyone using this popular supplement. While both can reduce the effectiveness of creatine and even introduce potential health risks, they occur due to different reasons and have distinct characteristics.
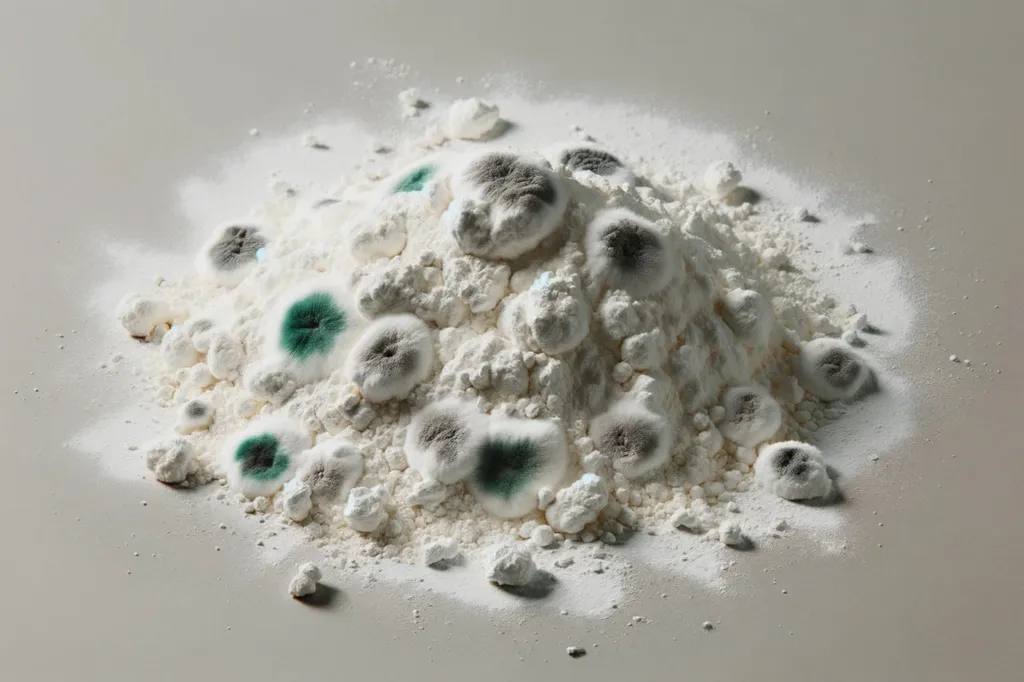
Creatine Degradation:
- What It Is: Over time, creatine can break down into its byproducts. This natural process is known as degradation. The primary byproduct of this process is creatinine.
- Causes: Exposure to moisture, heat, and prolonged storage can accelerate creatine degradation. Keeping creatine in a humid environment or storing it near a heat source can hasten its breakdown.
- Implications: Creatine that has undergone degradation loses its efficacy, meaning it might not offer the same energy boost or muscle performance benefits. Additionally, excessive creatinine, though naturally found in the body, can be taxing on the kidneys when present in larger amounts.
Creatine Contamination:
- What It Is: Contamination refers to the presence of unintended substances or impurities in the creatine supplement. These can be foreign particles, microbes, or other substances.
- Causes: Contamination can occur during the manufacturing process, packaging, or when the storage container is not sealed correctly, allowing foreign particles to enter. Additionally, using a wet scoop or storing creatine in a damp environment can introduce moisture, which can foster microbial growth.
- Implications: Consuming contaminated creatine can lead to health issues like digestive discomfort, infections, or allergic reactions. In the worst cases, contaminants can be toxic and pose serious health risks.
Key Takeaways:
- While degradation is a natural breakdown process, contamination is the introduction of foreign substances.
- Proper storage can prevent both degradation and contamination. Always store creatine in a cool, dry place and ensure the container is sealed tightly.
- If you suspect your creatine might be degraded or contaminated, it’s best to err on the side of caution and avoid consumption.
Maintaining Potency: Liquid vs. Powder Creatine
The potency and effectiveness of creatine can be influenced by its form—be it liquid or powder. Both forms have been widely debated in fitness communities regarding their stability and how well they deliver results. Let’s dive into the intricacies of liquid vs. powder creatine and how they maintain their potency.

Liquid Creatine:
- Stability Issues: Liquid creatine has been the subject of skepticism due to its stability. Some research suggests that creatine can begin to break down into creatinine (a less effective byproduct) when suspended in liquid for extended periods.
- Convenience: On the upside, liquid creatine is often favored for its convenience. There’s no need to mix it with water or any beverage, making it an on-the-go option for many.
- Absorption: Some proponents argue that liquid creatine allows for faster absorption in the body. However, scientific evidence on this claim remains inconclusive.
Powder Creatine:
- Higher Stability: Powdered creatine, especially creatine monohydrate, has shown to be more stable over time. This form is less prone to degradation when stored correctly, ensuring it maintains its potency.
- Versatility: Powdered creatine can be mixed with various beverages, allowing users to incorporate it into protein shakes, juices, or just plain water.
- Research-Backed: The majority of studies on creatine’s benefits have been conducted using the powdered form, particularly creatine monohydrate. As a result, its efficacy is well-documented and widely recognized.
Conclusion:
While both liquid and powder creatine have their own set of advantages, powdered creatine, particularly creatine monohydrate, appears to have the edge in terms of maintaining potency. However, individual preferences and lifestyle can influence the best choice for each user.
Other Supplements: Do They Expire Like Creatine?
When discussing the shelf life of supplements, it’s essential to recognize that each type varies in its stability and composition. Just like the question “does creatine expire,” many wonder about the expiration of other common supplements. Let’s explore the longevity and considerations for some of the most popular supplements on the market.

- Protein Powders:
- Most protein powders, like whey or casein, have an expiration date printed on the label. Generally, they remain effective for 12-18 months after being opened. However, if exposed to moisture, they can degrade faster and develop a rancid smell.
- Vitamins and Minerals:
- These supplements lose potency over time. After their expiration date, they might not offer the promised amount of nutrients. For example, vitamin C is particularly sensitive to light and air and can degrade faster than some other vitamins.
- Fish Oil:
- Fish oil capsules or liquid can go rancid if not stored correctly. An off-putting fishy smell is a clear sign that it’s time to discard them.
- BCAAs (Branched-Chain Amino Acids):
- Like creatine, BCAAs are relatively stable, especially in powder form. However, they should be consumed before their expiration date to ensure efficacy and safety.
- The potency of ingredients like caffeine or beta-alanine in pre-workout supplements can diminish over time. While they might not be harmful post-expiration, they might not provide the desired energy boost or performance enhancement.
- Herbal Supplements:
- The active ingredients in herbal supplements can lose potency with time. Factors like light, air, and moisture play a significant role in their degradation.
General Tips for Storing Supplements:
- Keep them in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
- Ensure the lids or seals are closed tightly after each use.
- Use a clean, dry scoop or spoon to prevent moisture introduction.
- Regularly check for changes in color, smell, or texture.
Conclusion:
While supplements like creatine have specific considerations regarding expiration, it’s a universal truth that all supplements degrade over time. It’s crucial to store them properly and be mindful of their expiration dates to ensure you’re getting the maximum benefits.
How Temperature and Humidity Affect Creatine Shelf Life
Understanding the effect of environmental conditions on supplements is pivotal to ensure their longevity and efficacy. The shelf life of creatine, like many other supplements, is significantly influenced by temperature and humidity. Let’s delve into how these factors play a role in determining the longevity and quality of your creatine supplement.

- Temperature:
- Stability: Creatine remains stable under typical room temperatures. However, prolonged exposure to high temperatures can accelerate the conversion of creatine to creatinine, a less effective byproduct.
- Storage Recommendations: It’s advisable to store creatine in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight or heat sources like stoves or heaters. If you live in an area with high temperatures, consider storing your creatine in a cupboard or pantry that remains consistently cool.
- Humidity:
- Moisture Concerns: Creatine is hygroscopic, meaning it can absorb moisture from the air. When exposed to high humidity levels, creatine can clump together, which might not only affect its texture but also its efficacy.
- Storage Recommendations: Always ensure the creatine container is sealed tightly. If your living environment is humid, it’s a good idea to store creatine in its original packaging with any included desiccant packets, or consider using airtight containers.
- Combined Effects of Temperature and Humidity:
- Warm and damp conditions create the perfect environment for microbial growth. In the unlikely event that moisture enters your creatine container and it’s stored in a warm place, there’s a risk of mold and bacterial growth, which could pose health risks.
- To safeguard against this, always check your creatine for any unusual odors, discolorations, or textures before consumption, especially if you suspect it might have been compromised.
Conclusion:
Temperature and humidity play a critical role in the shelf life and quality of creatine. By being conscious of storage conditions and ensuring your creatine is kept in a cool, dry environment, you can prolong its efficacy and reduce the risk of degradation or contamination.
Safety Precautions When Using Older Creatine
As with any supplement, safety should always be a primary concern. The age of creatine can affect its potency and safety, making it crucial to follow certain precautions when considering the use of older creatine. Let’s explore the safety measures one should adopt when faced with the decision of consuming aged creatine.

- Inspect Physical Appearance:
- Older creatine might undergo noticeable changes in texture. Fresh creatine powder is typically fine and free-flowing, but aged creatine exposed to moisture can clump together.
- Before consumption, visually inspect the creatine. If you notice any mold, discoloration, or any other unusual appearances, it’s best to discard it.
- Sniff Test:
- The sense of smell can be a powerful tool in detecting contamination. If your creatine emits an odd or rancid odor, this could be a sign that it’s degraded or has bacterial growth and should not be consumed.
- Taste Test (with Caution):
- If the creatine passes the visual and smell tests, you might consider a small taste test. Fresh creatine has a somewhat neutral taste. If the flavor is off or overly bitter, it’s a sign that the creatine has likely degraded into creatinine and should be discarded.
- Check the Expiry Date:
- While expiry dates are not always a definitive indicator of a product’s safety, they provide a guideline. If your creatine is past its expiration date, it’s wise to exercise extra caution and look for other signs of degradation.
- Limit Consumption:
- If you’re considering using older creatine that appears to be in good condition, it’s a good idea to start with a smaller dose to see how your body reacts before returning to your regular dosage.
- Store Properly:
- Even if the creatine is older, proper storage can still help in maintaining its quality. Always store it in a cool, dry place and ensure the container is sealed tightly to prevent any further degradation.
- Consult a Healthcare Professional:
- When in doubt, always consult with a healthcare or nutrition professional about the safety of consuming older supplements, including creatine.
Conclusion:
While older creatine can still be effective and safe for consumption, it’s essential to approach with caution. Following these safety precautions ensures that you prioritize your health and get the most benefit from your supplements.
Expert Opinions on Creatine Expiry
Creatine, being one of the most researched and popular sports supplements, has drawn the attention of many experts in the fields of nutrition, sports science, and health. Understanding the opinions of these professionals provides an informed perspective on the subject of creatine expiry. Here’s what some experts have to say:

- Stability of Creatine:
Dr. J. L. Wilson, a renowned nutritionist, points out that creatine’s chemical structure makes it relatively stable under standard storage conditions. However, prolonged exposure to high temperatures and moisture can compromise its integrity. - Degradation to Creatinine:
Nutrition expert Dr. M. Ratini emphasizes that over time, creatine can degrade to creatinine, a byproduct. This degradation is accelerated when creatine is exposed to liquids or humid environments. Creatinine, though a natural waste product of the body, isn’t beneficial as a supplement. - Safety of Aged Creatine:
Sports nutritionist Dr. S. Kleiner suggests that while consuming aged creatine might not be harmful, it could lose its efficacy. The body might not get the same performance-enhancing benefits from degraded creatine as from its fresher counterpart. - Importance of Storage:
Dr. J. Berardi highlights the critical role of storage in maintaining creatine’s potency. A cool, dry place is ideal, and it’s best to avoid storing creatine in the bathroom or other humid areas. - Expiry Date Considerations:
Registered Dietitian N. Rizzo points out that the expiry date is a manufacturer’s guarantee of the product’s potency and safety. While consuming a product shortly after this date might not pose health risks, its effectiveness might be diminished. - Recommendation on Liquid Creatine:
Dr. R. Kreider, a professor in exercise and sport nutrition, suggests skepticism regarding liquid creatine. He mentions that creatine’s stability in liquid form is questionable, and it may degrade faster than in powder form.
Experts generally agree that while creatine is a stable compound, its effectiveness can decrease over time, especially when not stored correctly. To get the most out of your creatine supplement, it’s best to adhere to storage guidelines and be mindful of the product’s age.
Conclusion
The world of supplements, particularly creatine, offers a plethora of benefits to fitness enthusiasts and athletes alike. However, like any other product, it comes with concerns, the most prominent being its shelf life. “Does creatine expire?” is a question that has garnered attention, especially given the supplement’s popularity. The answer, while simple, requires an understanding of its composition, storage, and degradation processes. While creatine does have a long shelf life, external factors such as temperature, moisture, and storage methods can influence its potency and safety.
Incorporating expert opinions and understanding the difference between creatine degradation and contamination is crucial. It’s evident that while consuming aged creatine might not pose significant health risks, its effectiveness could be compromised. Moreover, with numerous supplements available in the market, it’s essential to know that each might have its own unique expiry considerations, with storage and environmental factors playing pivotal roles.
In the journey towards achieving fitness goals, it’s of utmost importance to ensure that the fuel we provide our bodies is not just effective, but safe. By being informed, storing supplements properly, and regularly checking their condition, we can harness their full benefits while ensuring our well-being. As always, when in doubt about the state of your creatine or any supplement, consulting with a healthcare or nutrition expert is the best course of action.
Further Reading
For those wondering about the best ways to incorporate creatine into your routine, especially considering its timing and expiration, our article on creatine expiration pairs well with an insightful read from BodyBriks’ article, “How to Take Creatine Before Bed?,” offering a comprehensive understanding of effective creatine usage.
For additional reading and insights on the topic of creatine, here are some recommended resources:
- Creatine Supplementation for Muscle Growth: A Scoping Review – This article explores the effectiveness of creatine supplementation in different populations and its role in muscle growth and sports performance.
- Creatine for Exercise and Sports Performance, with Recovery – This study discusses the ergogenic benefits of creatine monohydrate, including enhanced strength, increased work capacity, and improved recovery.
- Common Questions and Misconceptions About Creatine Supplementation – This resource addresses various common questions and misconceptions related to creatine use, including its effects on kidney function and muscle cramping.
- Creatine Supplementation and Endurance Performance – An analysis of creatine’s role in enhancing exercise performance, particularly in endurance-based activities.
These resources provide a wide range of perspectives on creatine’s uses, benefits, potential side effects, and its role in physical performance enhancement.
Additionally, you’re invited to explore our collection of articles:





